Justin Stopa
Evolution of Swell
PostDoctoral Fellow: Dr Justin Stopa
Scientific Sponsors: Fabrice Ardhuin, Bertrand Chapron
LabexMER Research Axis 7: Sea motions and interactions with marine structures
Forecasting and hindcasting marine conditions with sufficient detail have assumed a greater importance with societal impacts and scientific advancements. Wave dissipation plays a significant role in the evolution of waves despite e-folding scales as large as 20,000 km. The focus here is in dissipation due to non-breaking actions. Since the behavior of the decay is non-linear, laminar-to-turbulent boundary layer has been proposed as a plausible mechanism. While the physical mechanism causing the decay is still under debate, swell attenuation rates have been estimated from remotely sensed synthetic aperture radar (SAR). These previous studies were limited in quality of the measurements as well as quantity of events so focus is paid to extrapolating the number of cases and the improvement of the SAR observations. As ice continues to melt, larger expanses of ocean are open for wave development. Wave-ice interaction can play an important role in ice floe break-up and it is expected that similar mechanisms are responsible for the dissipation. The results will be directly implemented in a spectral wave model to improve our ability to describe the sea state.
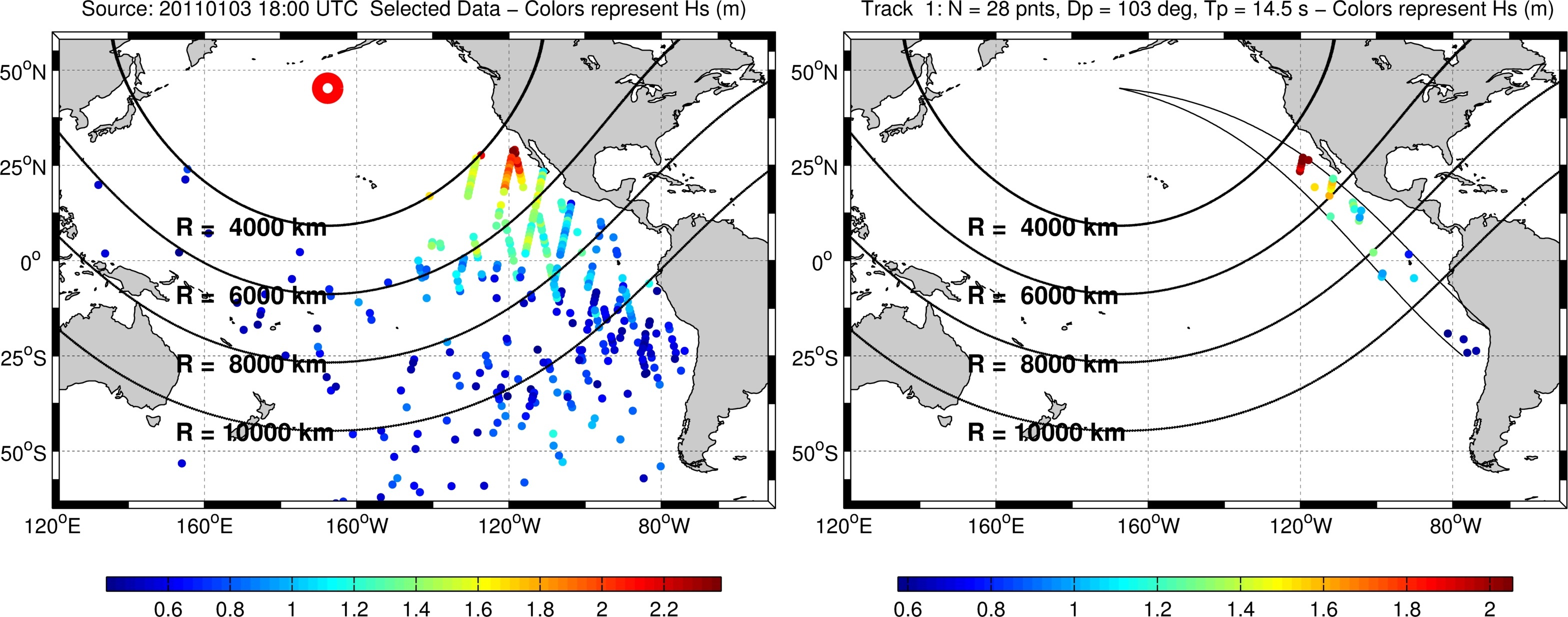 Figure 1
Figure 1
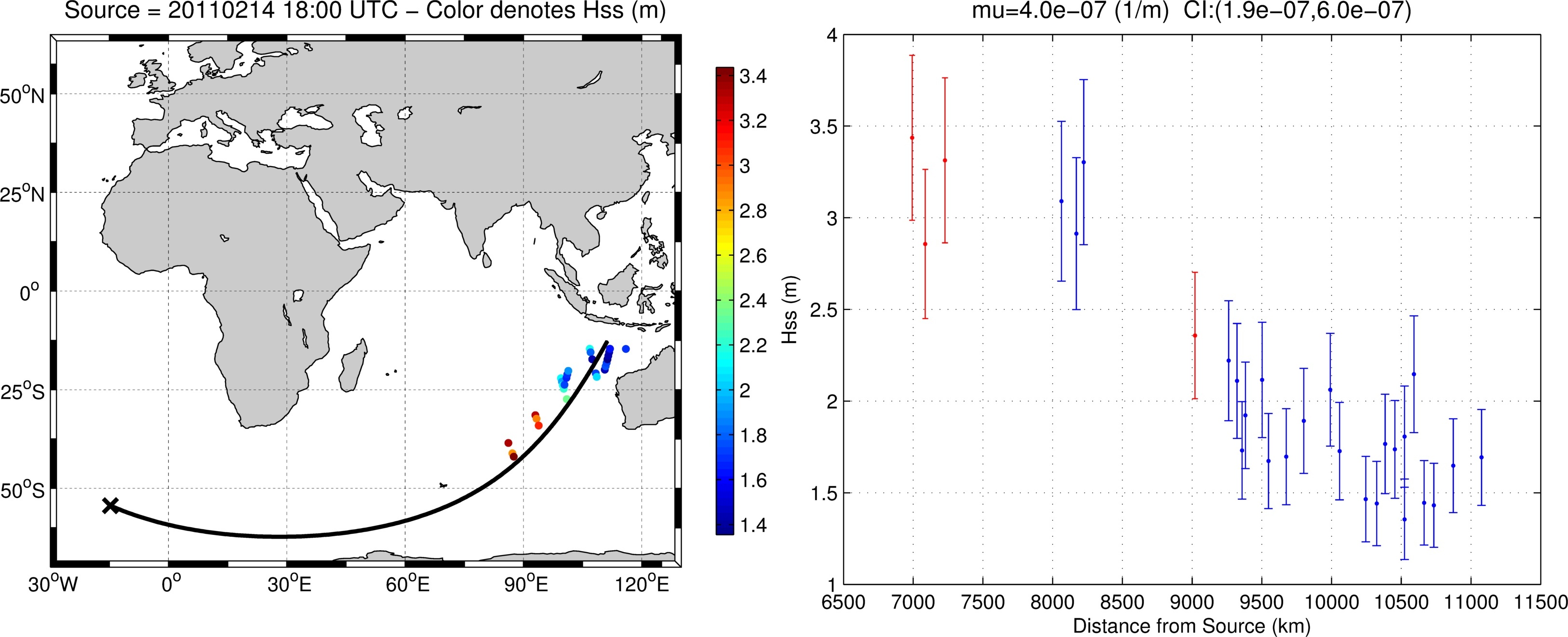
Figure 2
Document Actions











